A large part of the 3D printers we have is not based on filament but on powder. Laser sintering, Multi Jet Fusion and Metal 3D Printing is used to create 3D prints in materials such as polyamide, alumide, titanium, and rubber-like.
The interior of the printer is heated up to just below the melting point of the powder of your choice. The printer then spreads out an incredibly fine layer of this powder. A laser beam heats up the areas that need to be sintered together just above the melting point. The parts that were touched by the laser are now fused together while the rest continues to remain loose powder.
The models are printed layer by layer with the help of this laser beam. After a layer is printed, a new layer of fresh powder is spread over the surface by a roller. After the printing job is finished, the result is a big block of powder that contains the printed (sintered) models inside. In order to get your prints out of the powder block, we need to dig into the box of un-sintered powder and brush away the excess.
One reason why this is a great technology is that no supporting structure is needed. The un-sintered powder is the supporting material. This allows for complex designs, and even interlinking and moving parts.
Powder- & Binder-based 3D Printing
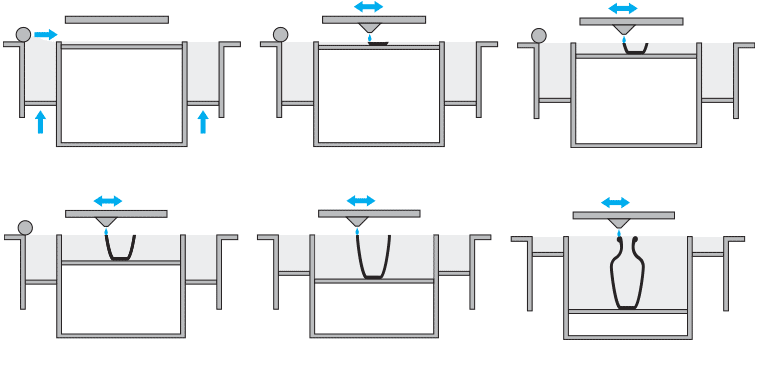
Other materials such as steel also rely on powder but are not laser sintered. Instead, a binder is used to "glue" parts together. We refer to this technology as “Powder- & Binder-based 3D Printing”.
The starting process of this technology is quite similar to laser sintering: a roller puts a thin layer of powder on a platform. However, instead of a laser beam, a special print head places a binding agent at specific points, printing a thin layer of your model that is able to bind to subsequent layers. This process is then repeated over and over again until your model is complete.
Since your model was only "glued" together, some post-processing is necessary with this 3D printing technology. The exact post-processing steps heavily depend on the material: Steel models are additionally infused with bronze for extra strength.