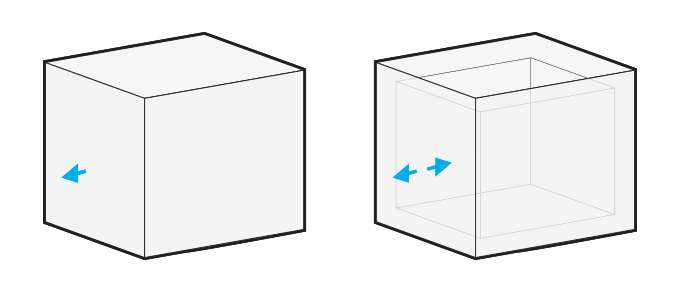
Normals are perpendicular reference points to surfaces on 3D models. They define whether the surface is an inside or outside face (closed set of edges).
An inverted normal is a normal that is pointing in the wrong direction, telling the computer that an outside face is actually an inside face when it isn’t. If you have a hollow design, an inverted normal can be indicated as you have both surfaces facing in and out in the same model.